1H, 13C and 15N resonance assignments of the second peptidyl-prolyl isomerase domain of chaperone SurA from Escherichia coli
发布日期:2019年12月18日 09:58 点击:
Biomol NMR Assign. 2019 Apr;13(1):183-186. doi: 10.1007/s12104-019-09874-1. Epub 2019 Jan 25.
1H, 13C and 15N resonance assignments of the second peptidyl-prolyl isomerase domain of chaperone SurA from Escherichia coli.
Abstract
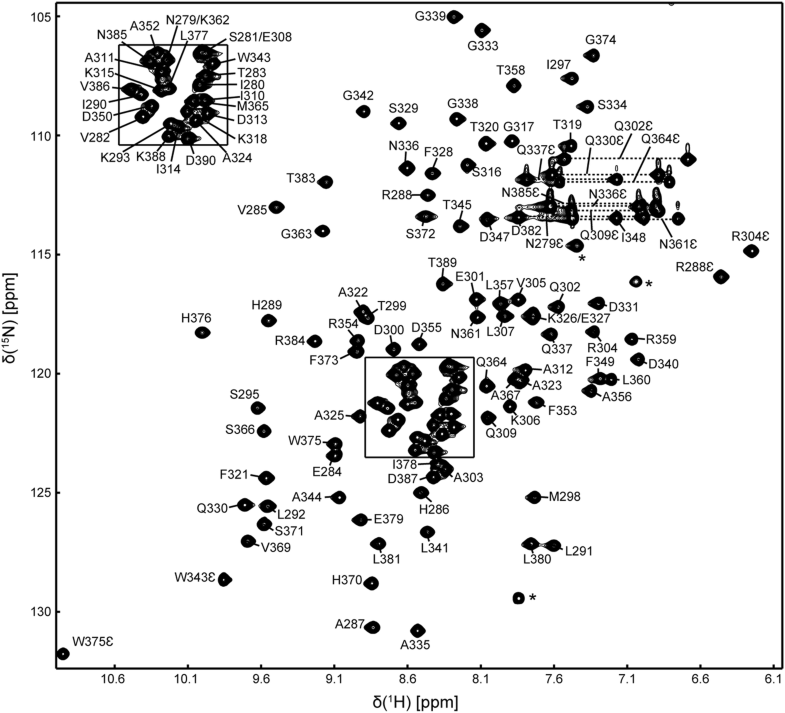
The periplasmic chaperone SurA in Gram-negative bacteria plays a central role in the biogenesis of integral outer membrane proteins and is critical to the maintenance of bacterial membrane integrity. SurA contains a core chaperone module comprising the N- and C-terminal domains, along with two peptidyl-prolyl isomerase (PPIase) domains. The chaperone activity of SurA has been demonstrated to rely on the core module, whereas recent works suggested that the PPIase domains may regulate the chaperone activity through large conformational rearrangements. Herein, we report the resonance assignments of 1H, 13C and 15N atoms of the second PPIase domain of Escherichia coli SurA, which provide valuable information for further studies of the structure, dynamics and interactions of this chaperone using NMR techniques.